Theory
Introduction
The experiment, Read and Write Operations in Random Access Memory (RAM), explores the fundamental principles of data storage and retrieval in a digital computing system. RAM is a type of volatile memory used to temporarily store data that the processor accesses during execution. Understanding the read and write operations is crucial as these are the primary mechanisms through which data is handled in memory.
The write operation involves storing a specific value at a designated memory address, while the read operation retrieves the value stored at a particular address.
Aim:
To perform and understand the read and write operations in a Random Access Memory (RAM) module by simulating input and output connections, and verifying data storage and retrieval.
RAM:
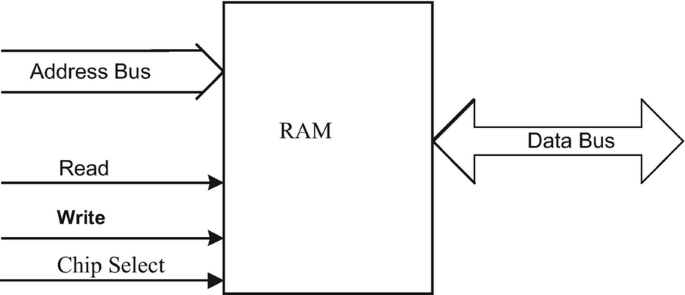
Random Access Memory (RAM) is a type of volatile memory used for temporary data storage. It allows both read and write operations. Data is stored in memory cells located at specific addresses.
Key operations:
1 - Write Operation: Data is written into a specific memory address when the Write bit (Wr) is activated.
2 - Read Operation: Data stored at a specific memory address is retrieved when the Read bit (Rd) is activated.
1 - RAM module simulation tool
2 - Input switches/buttons for data bits
3 - Address switches/buttons for address bits
4 - Control switches/buttons for Clock (Cs), Read (Rd), and Write (Wr)
5 - Output indicators for data bits
Principle:
RAM works on the principle of data storage in memory cells, each identified by a unique address. Data is written to or read from these cells based on control signals. Activation of the clock signal ensures synchronization of operations.
Working:
1 - Write Operation:
• Input data and target address are specified.
• When the Write signal is activated, the data is stored in the memory cell corresponding to the address.
2 - Read Operation:
• Target address is specified.
• When the Read signal is activated, data stored in the memory cell at the specified address is retrieved and sent to the output lines.
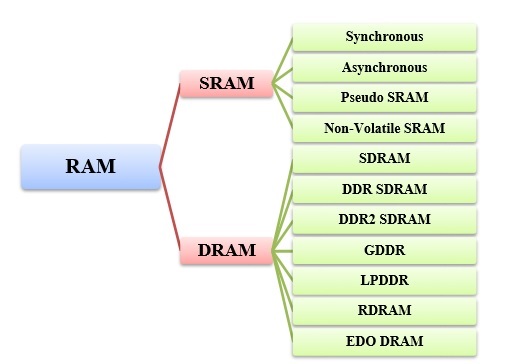
Types of RAM:
1 -Static RAM (SRAM):
• Data is stored using flip-flops.
• Faster but more expensive and requires more power.
2 - Dynamic RAM (DRAM):
• Data is stored using capacitors.
• Slower but more cost-effective and consumes less power.
Applications of RAM:
1 - Computer Systems:• RAM is used as main memory for temporary data storage during program execution.
2 - Embedded Systems:• RAM is used as main memory for temporary data storage during program execution.
3 - Graphics Processing:• RAM is used as main memory for temporary data storage during program execution.
4 - Caching:• RAM is used as main memory for temporary data storage during program execution.
Observations:
• During the Write operation, data provided on the input lines is successfully stored in the RAM at the specified address.
• During the Read operation, the stored data is accurately retrieved and displayed on the output lines.
Result:
The read and write operations in the RAM module were successfully demonstrated. Data was accurately written to and retrieved from the specified memory addresses, confirming the functionality of the RAM.
Conclusion: The experiment verified the working principles of RAM, demonstrating its ability to store and retrieve data based on input address and control signals. The successful execution of read and write operations illustrates the practical use of RAM in data storage and processing systems.
